A shared vocabulary about the capabilities of each new tool and technique is crucial as AI transforms our technological world. Common vocabularies establish shared intellectual spaces that enable all participants to improve adoption, foster cooperation, assess development, and promote innovation.
The Turing Test is the AI benchmarking tool that is currently the most well-known.
However, since the Turing Test’s beginnings in 1950, the field of artificial intelligence (AI) has advanced significantly. As a result, it is increasingly evident that the Turing Test is inadequate for assessing the complete spectrum of AI capabilities that are currently emerging or are anticipated to do so in the future.
The Turing Test has a crude pass/fail system and places a lot of emphasis on chat/linguistic abilities, which is merely one component of human intellect. Numerous other crucial aspects of intelligence, like problem-solving, creativity, and social awareness, are ignored by this restricted emphasis on language. Furthermore, the Turing Test assumes a level of intelligence comparable to that of humans, which may not be pertinent or helpful for judging AI.
The structure
It is important and crucial to establish a more sophisticated and thorough methodology for assessing AI capabilities across several dimensions of intelligence in order to address these constraints.
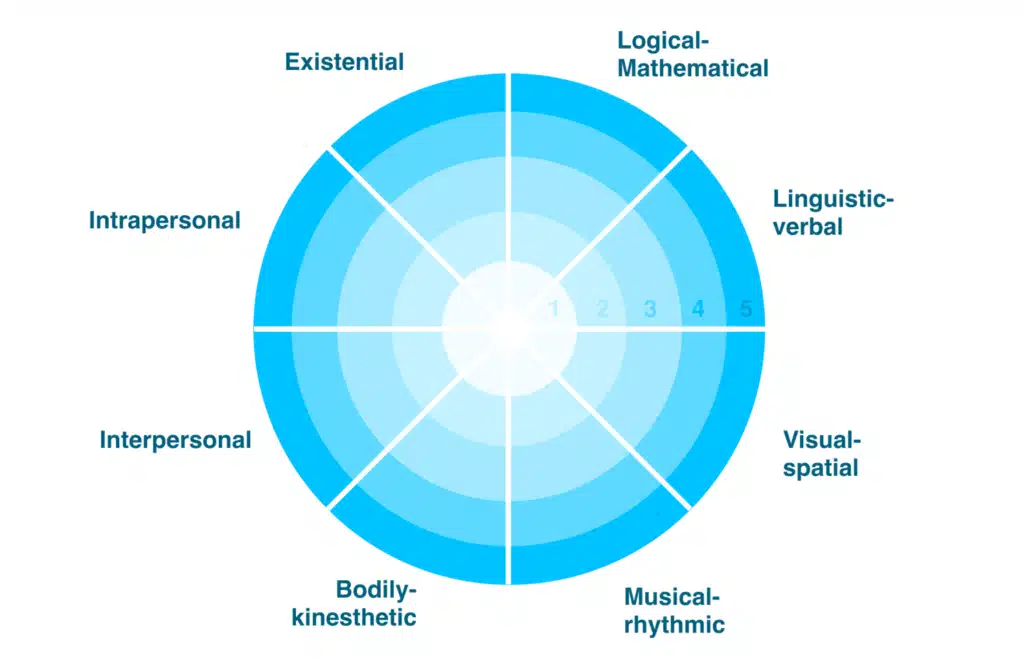
I came up with the “AI Classification Framework” as a result of this realization. The Theory of Multiple Intelligences serves as the foundation for the ACF, a novel methodology for assessing AI capabilities.
Howard Gardner, a psychologist, initially put forth the Theory of Multiple Intelligences in 1983. Gardner maintained that intelligence was a collection of diverse skills that may appear in a variety of ways rather than a single, cohesive entity. Gardner distinguished eight categories of intelligence: Gardner claims that each form of intelligence is distinct from the others and that people can be exceptionally gifted in one or more of these categories. The idea provided fresh perspectives for examining the variety of human cognition while challenging the conventional conception of intelligence as a single, unchanging thing.
Despite some criticism and controversy over the years, the notion of multiple intelligences has had a substantial impact on psychology and education, particularly in the creation of alternative teaching and learning methods.
As a foundation for the AI Classification Framework, this appeared ideal. The framework, which is in line with the theory, encourages the evaluation of AI tools in terms of linguistic, logical-mathematical, musical, spatial, bodily-kinesthetic, interpersonal, and intrapersonal intelligence.
The framework offers a scale from 1 to 5 for each aspect of intelligence, with 1 denoting “No Capability” or the equivalent of a human neonate, and 5 denoting “Self-agency” or a potential for what might be called “Super Intelligence” — intellect that is beyond and beyond human capacity.
Examples
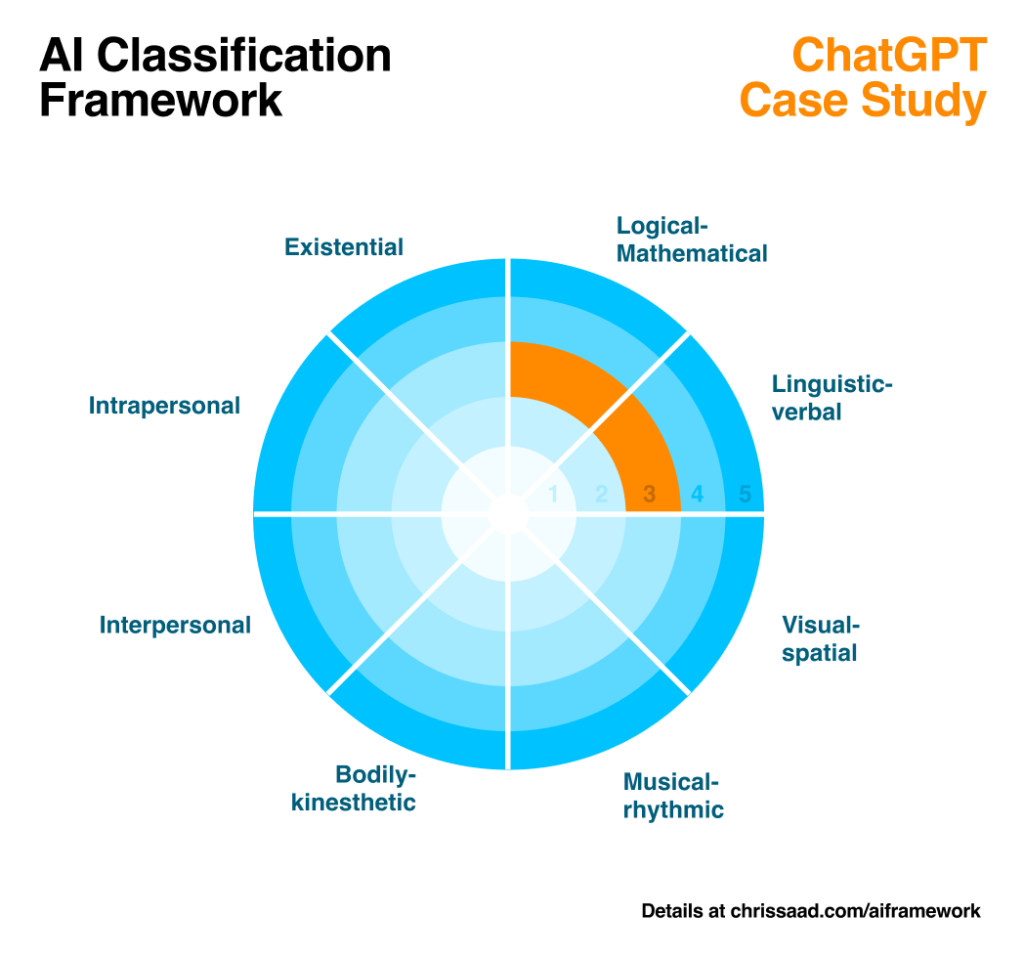
The framework itself is presented here as a thorough table of descriptions. For quick high-level reference, I’ve also produced a straightforward visual representation. Here are two brief samples of segments that work with ChatGPT and DALL-E 2’s features.
ALSO READ THIS: Review of the 2023 Opel Grandland GSe

